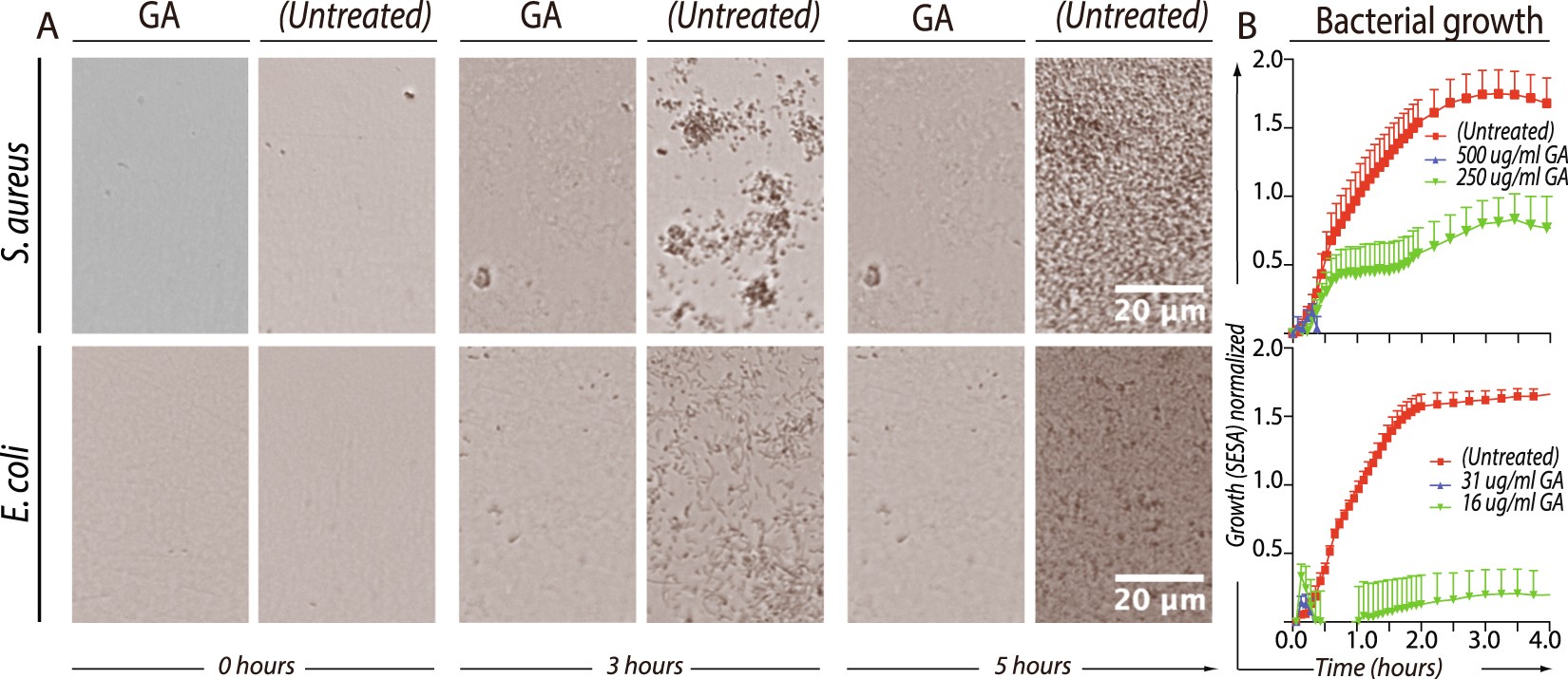
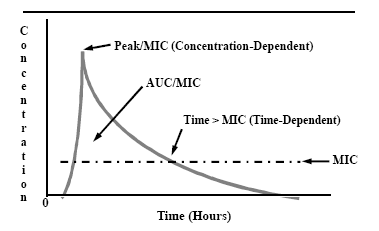
The breakpoint panel is when only one or a few concentrations of each antimicrobial agent are tested on a single panel. The measurement of antibiotic concentrations in various fluids has been a prominent aspect of the evaluation of new antibiotics and the quality control of their manufacture.

Applications Significance Of And Methods For The
Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids biologic assays. The concentrations of the respective drugs in simultaneously collected samples of fluid from each diffusion chamber were measured and compared with concentrations found at the same time in serum. In most cases the so called therapeutic concentration means that the local concentration of the antimicrobial agent should be at least equal to if not greater than the minimal inhibitory concentration of the infecting organism. High performance liquid chromatography hplc. All serum results are referred to standard curves established with serumdiluents. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobials may be important when treatment includes agents that have a narrow margin between their therapeutic and their toxic levels such as the aminoglycosides especially gentamicin or.
Applications significance of and methods for the measurement of antimicrobial concentrations in human body fluids. All chambers were tolerated well and the method proved to be effective for collecting data on the distribution of drugs throughout the body. In contrast dilution methods allow determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of an agent which can be correlated with blood urine and other body fluid levels of the antimicrobial agent. Humanserum pools are prepared from serumcol. Use of antibiotics to measure amount of antimicrobial agents chromatographic assays. The measurement of the antibiotic concentration in body fluids and tissue samples makes it possible to determine whether the drug concentration at the site of infection is high enough when compared with the mic value and thus to predict the therapeutic effect.
Occasionally aminoglycoside concentrations have been measured in other body fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid csf to assess the degree of antibiotic penetration into the space or to assure adequate intrathecal dosing 64 65 66. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important when the margin between therapeutic and toxic levels is narrow such as for aminoglycosides or vancomycin and when a patient has renal failure and may have accumulation of high levels of antimicrobial agents. Human serum samples containing unknown con centrations ofan antimicrobial are assayed as above but a normal human serum pool is used as diluent. Determination of serum bactericidal activity is in effect an assay of the activity of antimicrobial containing serum. The breakpoint is the term applied to the concentration of an antimicrobial agent that coincides with a susceptible or intermediate mic break point for a particular drug. The reference standard concentration is also pre pared in a normal human serum pool.
Focus on finding the biologically active amount of drug immunoassays. With the development of various assay techniques the total amount of antimicrobial agent in serum as well as in urine cerebrospinal fluid csf and other body fluids can be measured. It indirectly measures the combined effects of susceptibility of the test organism and serum concentration of the antimicrobial agent. With the availability of rapid accurate assays the measurement of antibiotic material in serum and other body fluids is feasible desirable and widely practiced for these purposes.