Understanding how radiation is measured with geiger counter and scintillation crystal technology. Geiger mueller gm tube sensing element.

Radioactivity Experiments To Determine The Penetrating Power
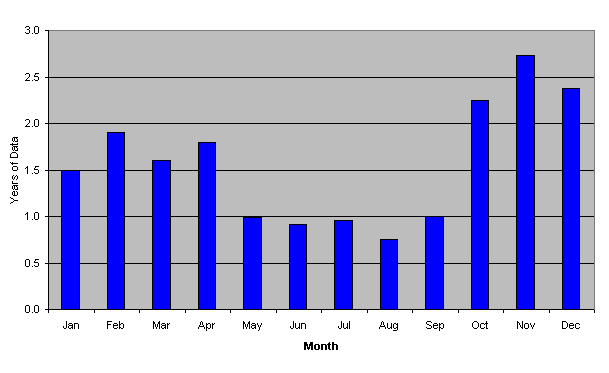
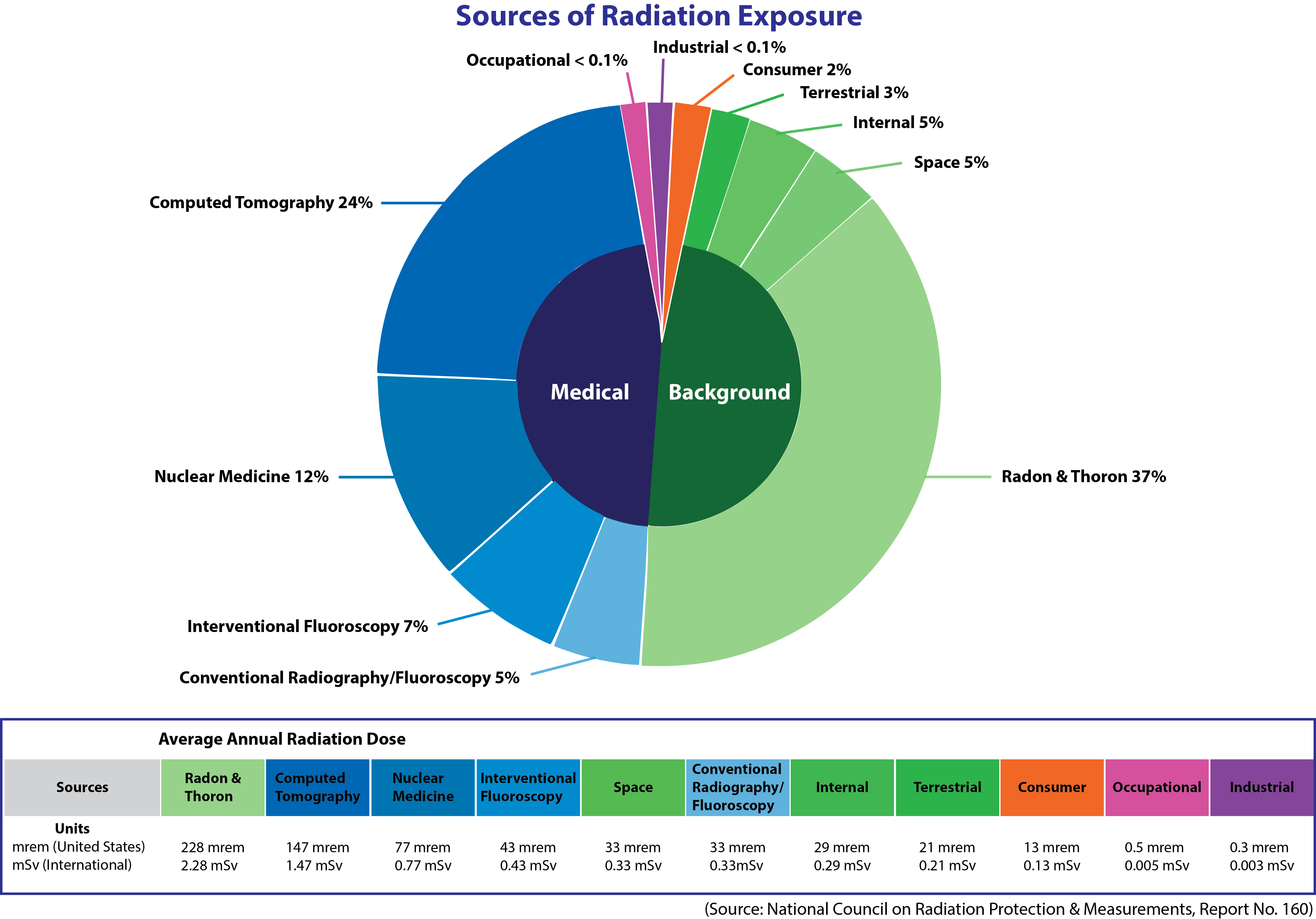
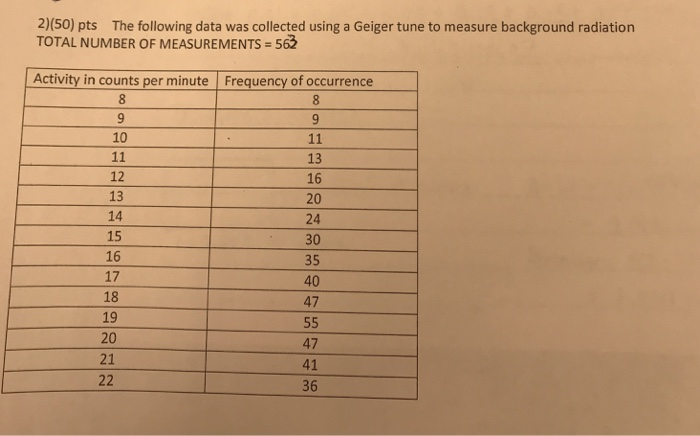
How is background radiation measured. Measuring amounts of radiation. Background radiation is any radiation detected by the gamma ray spectrometer not originating from the source that is being analyzed in this case the lithosphere iaea 1976. The sensing element is the heart of the detector. Weather conditions also affect radiation levels as snow cover may shield these elements and radioactive particulates can wash out of the air during rain storms. The general publics understanding of ionizing radiation is limited 1. Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
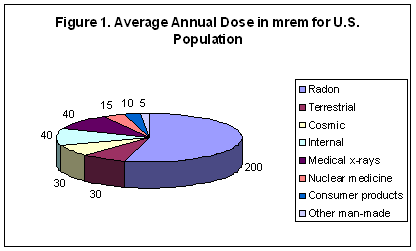
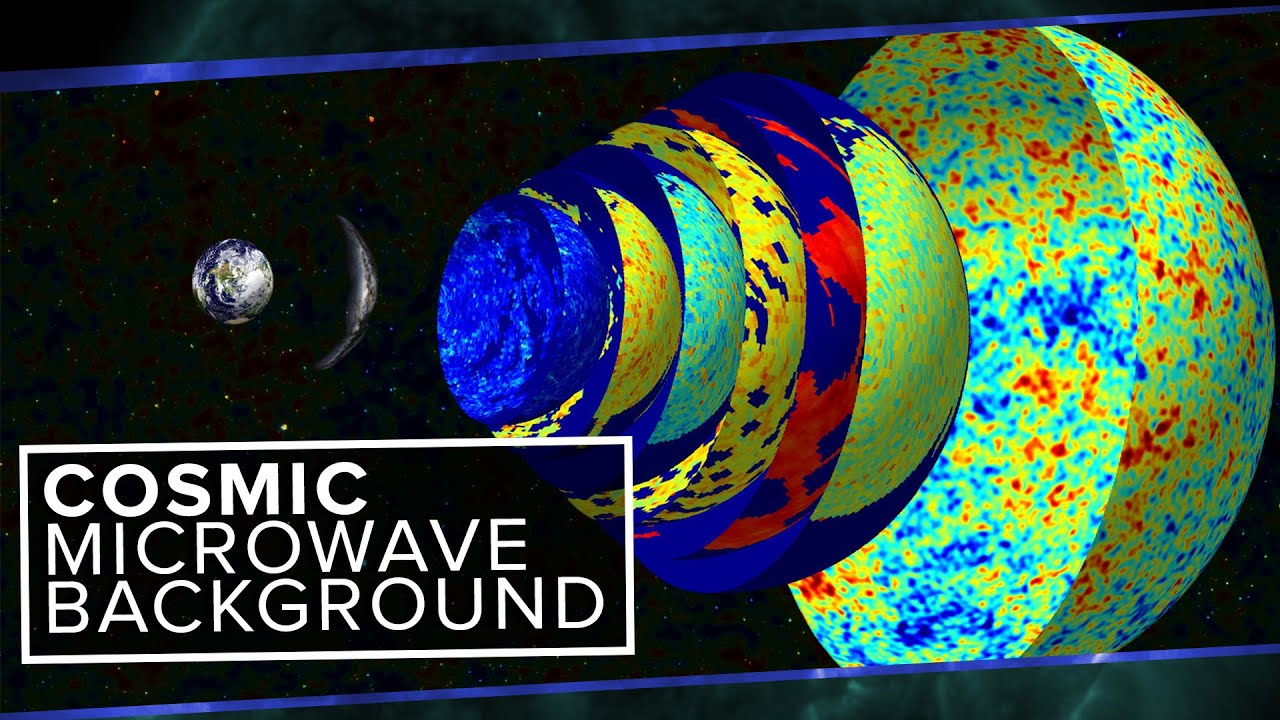
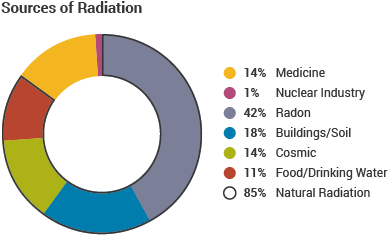
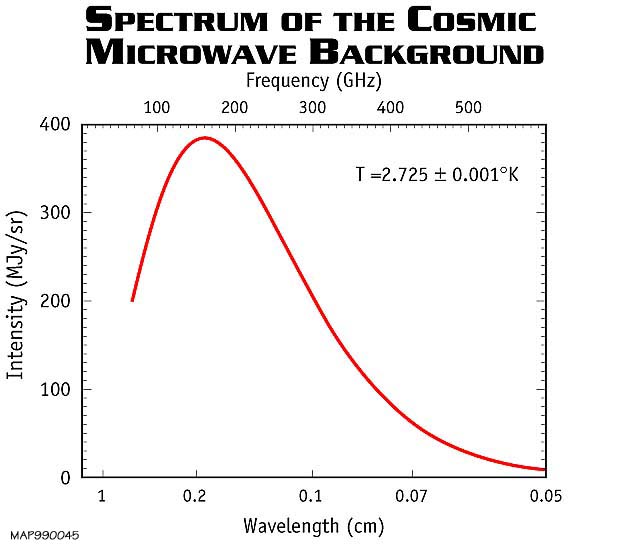
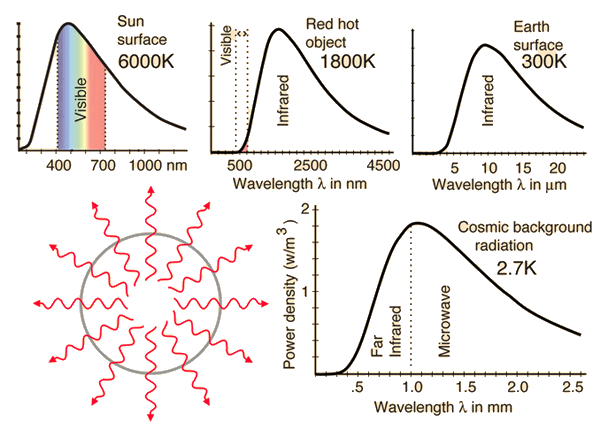
The digital geiger counter is a particle detector that could detect alpha beta and gamma radiations although it detects gamma ray with lower sensitivity compared to other detectors. The cosmic microwave background radiation is an emission of uniform black body thermal energy coming from all parts of the sky. Are used in most portable hand held survey detectors to locate radiation. Exposing a patient to radiation is a measured justified means aiding patient careeach medical imaging examination utilizing ionizing radiation adheres to the fundamental principles of radiation protection. These include both cosmic radiation and environmental radioactivity from naturally occurring radioactive materials as well as man made medical x rays fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents. Background radiation originates from a variety of sources both natural and artificial.
There are primarily two types of detector sensor technologies that are used. This article provides a basic comparison of common medical imaging examinations in contrast to natural background. The biological risk of exposure to radiation is measured using the conventional unit rem or the si unit sievert sv. In the case of a laboratory spectrometer it includes radiation coming from or through the walls ceiling and floor and the lead counting chamber or shield. This instrument is capable of measuring the natural background radiation nbr rates in one count per minutes cpm. Cosmic radiation from the.
Measuring radiation there are four different but interrelated units for measuring radioactivity exposure absorbed dose and dose equivalent. Background radiation varies from place to place and over time depending on the amount of naturally occurring radioactive elements in soil water and air. The radiation is isotropic to roughly one part in 100000. These can be remembered by the mnemonic r e a d as follows with both common british eg ci and international metric eg bq units in use. The radiation dose absorbed by a person that is the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation is measured using the conventional unit rad or the si unit gray gy. The root mean square variations are only 18 µk after subtracting out a dipole anisotropy from the doppler shift of the background.
Background radiation affects everyone mainly by irradiation but a small amount is from being contaminated by radioisotopes in the food and drink that is consumed.