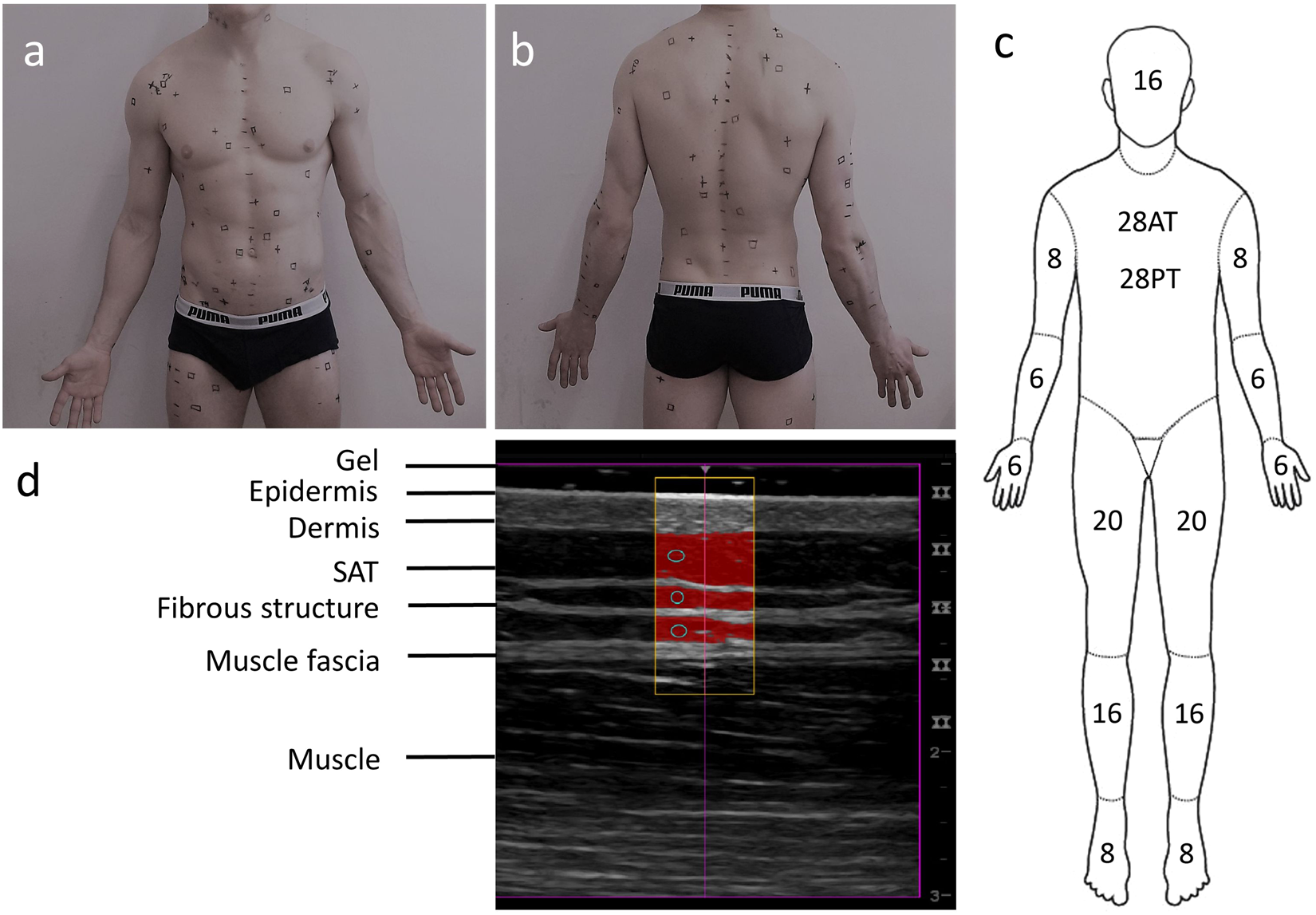
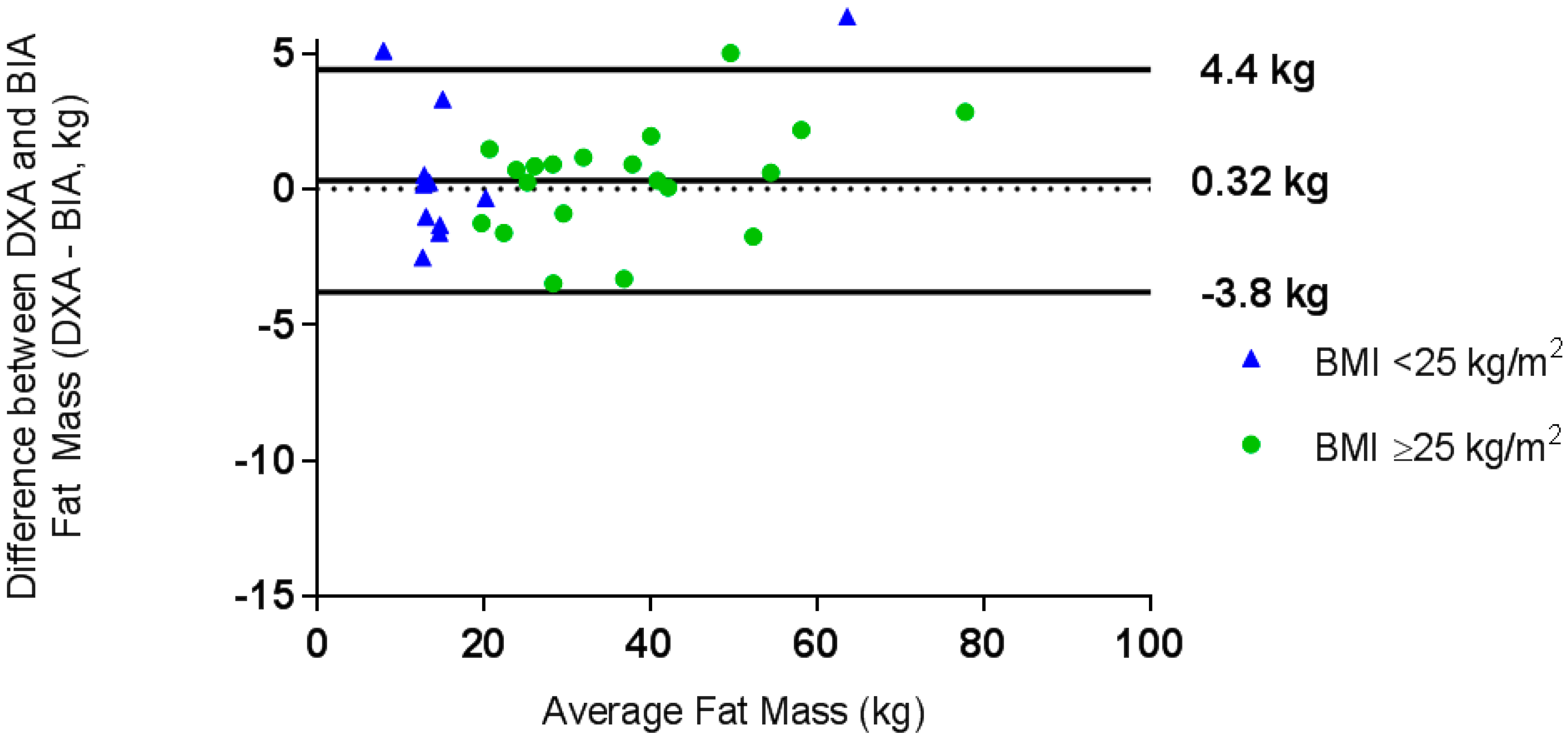
A simple three compartment model combining measurements of body density by air displacement plethysmography and total body water by bio electrical impedance can provide measurements of percentage body fat in the severely obese that are comparable with a traditional highly technical three compartment model requiring facilities such as. Recent findings there is little published research regarding what body composition methods can be used with confidence in the severely obese populations.
Obesity Paradox And Blood Transfusions Research Specialtycare
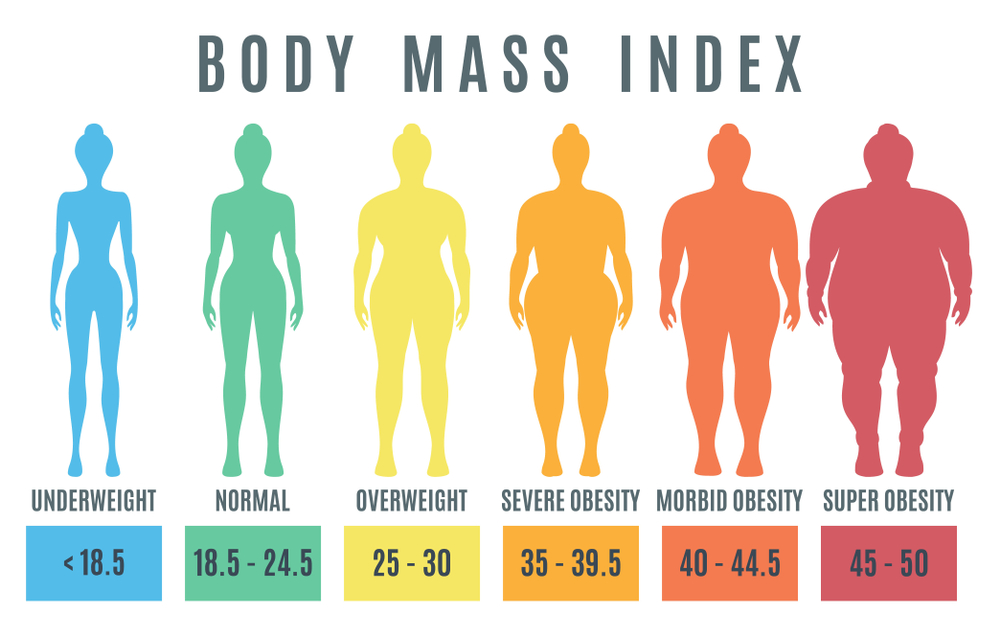
Body composition measurement in severe obesity. Therefore we examined differences in body. Class 3 obesity is sometimes categorized as extreme or severe obesity. This review focuses on some of the methodological and practical issues associated with the use of common body composition methods and identifies available published information on feasible methods for use in the severely obese. Body composition measurement in severe obesity. Bmi of 40 or higher. 1energy metabolism laboratory jean mayer usda human nutrition research center on aging at tufts university boston massachusetts 02111 usa.
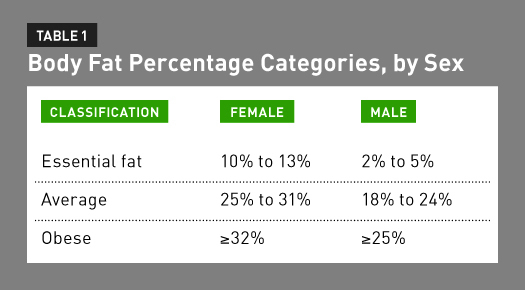
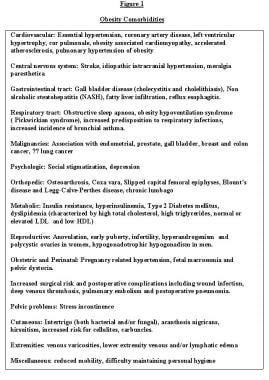
The physical size limitations imposed by severe obesity and variations in body composition from that of normal weight pose tremendous challenges to the measurement of body composition. G6 body composition analysis scales are sophisticated yet affordable devices that help physicians address obesity and fitness in their patient populations. The physical size limitations imposed by severe obesity and variations in body composition from that of normal weight pose tremendous challenges to the measurement of body composition. At an individual level bmi can be used as a screening tool but is not diagnostic of the body fatness or the health of an individual. Performing a detailed body composition analysis and educating patients about the results provides a valuable service that can impact patient health while helping physician practices grow. Bmi of 35 to 40.
Severe obesity is accompanied by large increases in fat massand alterations in the composition of fat free mass in particular total bodywater and its extracellular compartment. Obesity in early childhood is associated with increased risk of chronic diseases but studies of body composition at preschool ages are sparse.